Cuts and Goals
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
| > Advanced Programming Techniques > Using Goals > Cuts and Goals |
Cuts and Goals |
INDEX
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
|
Goals can also be used to add global cuts. Whereas local cuts are respected only in a subtree, global cuts are added to the entire problem and are therefore respected at every node after they have been added.
Global cuts can be added similarly to local cuts by using a global cut goal. A global cut goal is created with method IloCplex::GoalI::GlobalCutGoal (IloCplex.globalCutGoal). This method takes an IloRange or an IloRangeArray (IloRange[]) object as its parameter and returns a goal. When the goal executes, it adds the constraints as global cuts to the problem.
Example ilogoalex2.cpp shows the use of IloCplex::GoalI::GlobalCutGoal for solving the noswot MILP model. This is a relatively small model from the MIPLIB 3.0 test set, consisting only of 128 variables. Nonetheless, it is very hard to solve without adding special cuts.
Although it is now solvable directly, the computation time is in the order of several hours on state-of-the-art computers. However, cuts can be derived, and the addition of these cuts makes the problem solvable in a matter of minutes or seconds. These cuts are:
These cuts have been derived after interpreting the model as a resource allocation model on five machines with scheduling, horizon constraints, and transaction times. The first three cuts break symmetries among the machines, while the others capture minimum bounds on transaction costs.
Of course the best way to solve the noswot model with these cuts is to simply add them to the model before calling the optimizer. However, for demonstration purposes, the cuts are added by means of a goal. The source code of this example can be found in the examples/src directory of the ILOG CPLEX distribution. The equivalent Java version appears as GoalEx2.java in the same location.
The goal CutGoal in this example receives a list of "less than" constraints to use as global cuts and a tolerance value eps. The constraints are passed to the goal as an array of lhs expressions and an array of corresponding rhs values. Both are initialized in function makeCuts.
The goal CutGoal checks whether any of the constraints passed to it are violated by more than the tolerance value. It adds violated constraints as global cuts. Other than that, it follows the branching strategy IloCplex would use on its own.
The goal starts out by checking if the solution of the continuous relaxation of the current node subproblem is integer feasible. This is done by calling method isIntegerFeasible. If the current solution is integer feasible, a candidate for a new incumbent has been found and the goal returns the empty goal to instruct IloCplex to continue on its own.
Otherwise, the goal checks if any of the constraints passed to it are violated. It computes the value of every lhs expression for current solution by calling getValue(lhs[i]). The result is compared against the corresponding rhs value rhs[i]. If a violation of more than eps is detected, the constraint is added as a global cut and the rhs value will be set to IloInfinity to avoid checking it again unnecessarily.
The global cut goal for lhs[i] 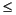
rhs[i] is created by calling method GlobalCutGoal. It is then combined with goal goal using method AndGoal, so that the new global cut goal will be executed first. The resulting goal is stored again in variable goal. Before adding any global cut goals, variable goal is initialized as
IloCplex::Goal goal = AndGoal(BranchAsCplexGoal(getEnv()), this); |
for C++, or for Java:
cplex.and(cplex.branchAsCplex(), this); |
The method BranchAsCplexGoal(getEnv) ((cplex.branchAsCplex) creates a goal that branches in the same way as the built-in branch procedure. By adding this goal, the current goal will be executed for the entire subtree.
Thus the goal returned by CutGoal will add all currently violated constraints as global cuts one by one. Then it will branch in the way IloCplex would branch without any goals and execute the CutGoal again in the child nodes.
| Copyright © 1987-2003 ILOG, S.A. All rights reserved. Legal terms. | PREVIOUS NEXT |