This function returns a constraint that abstracts the values of the
elements of one array of constrained variables (called x) in a
model into the abstract value of another array of constrained variables
(called y). In other words, for each element x[i],
there is a variable y[i] corresponding to the abstraction of
x[i] with respect to an array of numeric
values. That is,
x[i] = v with v in values if and
only if y[i] = v;
x[i] = v with v not in values if
and only if y[i] = abstractValue.
This constraint maintains a many-to-one mapping that makes it possible to
define constraints that impinge only on a particular set of values from the
domains of constrained variables. The abstract value (indicated by
abstractValue) must not be in the domain of
x[i].
Adding a Constraint to a Model, Extracting a Model for an Algorithm
In order for the constraint returned by IloAbstraction to
take effect, you must add it to a model with the template IloAdd or the member function IloModel::add and extract the model for an algorithm with the
member function IloAlgorithm::extract.
Exceptions
If the arrays x and y are not the same size,
this function throws the exception
IloAbstraction::InvalidArraysException.
Example
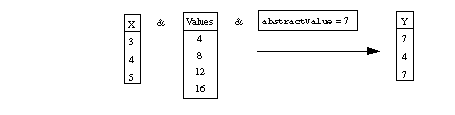
For simplicity, let's assume that our array x consists of
three elements with the domains {3}, {4}, and {5}. We will also assume that
our abstract value is 7, and the values we are interested in
are {4, 8, 12, 16}. Then IloAbstraction produces these elements
in the array y: