Example: Network Optimizer in the Interactive Optimizer
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
| > Continuous Optimization > Solving Network-Flow Problems > Example: Network Optimizer in the Interactive Optimizer |
Example: Network Optimizer in the Interactive Optimizer |
INDEX
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
|
This example is based on a network where the aim is to minimize cost and where the flow through the network has both cost and capacity. Figure 10.1 shows you the nodes and arcs of this network. The nodes are labeled by their identifying node number from 1 through 8. The number inside a node indicates its supply value; 0 (zero) is assumed where no number is given. The arcs are labeled 1 through 14. The lower bound l, upper bound u, and objective value c of each arc are displayed in parentheses (l, u, c) beside each arc. In this example, node 1 and node 5 are sources, representing a positive net flow, whereas node 4 and node 8 are sinks, representing negative net flow.
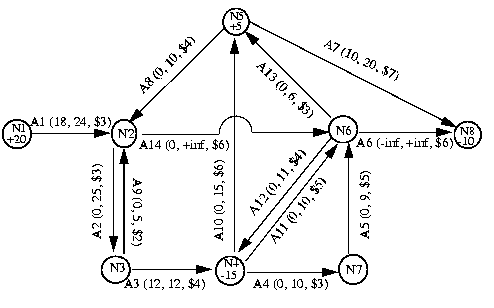
In the standard distribution of ILOG CPLEX, the file nexample.net contains the formatted problem formulation for this example. You can read it into the Interactive Optimizer with the command read nexample.net. After you read the problem into the Interactive Optimizer, you can solve it with the command netopt or the command optimize.
| Copyright © 1987-2003 ILOG, S.A. All rights reserved. Legal terms. | PREVIOUS NEXT |